Comprehensive analysis of DC resistance, saturation behavior, and thermal performance for power inductor qualification.
Bench tests show typical DC resistance and saturation behavior for 7847709100 under rated currents — this report aggregates those measurements and explains what they mean for design. The summary emphasizes practical specifications, representative test data, and qualification steps so design and QA teams can act on measurable criteria.
Scope: Electrical specifications, thermal and mechanical ratings, test methodology, representative measurement tables and curves, interpretation of deviations, and an application/qualification checklist.
Product Background & Overview

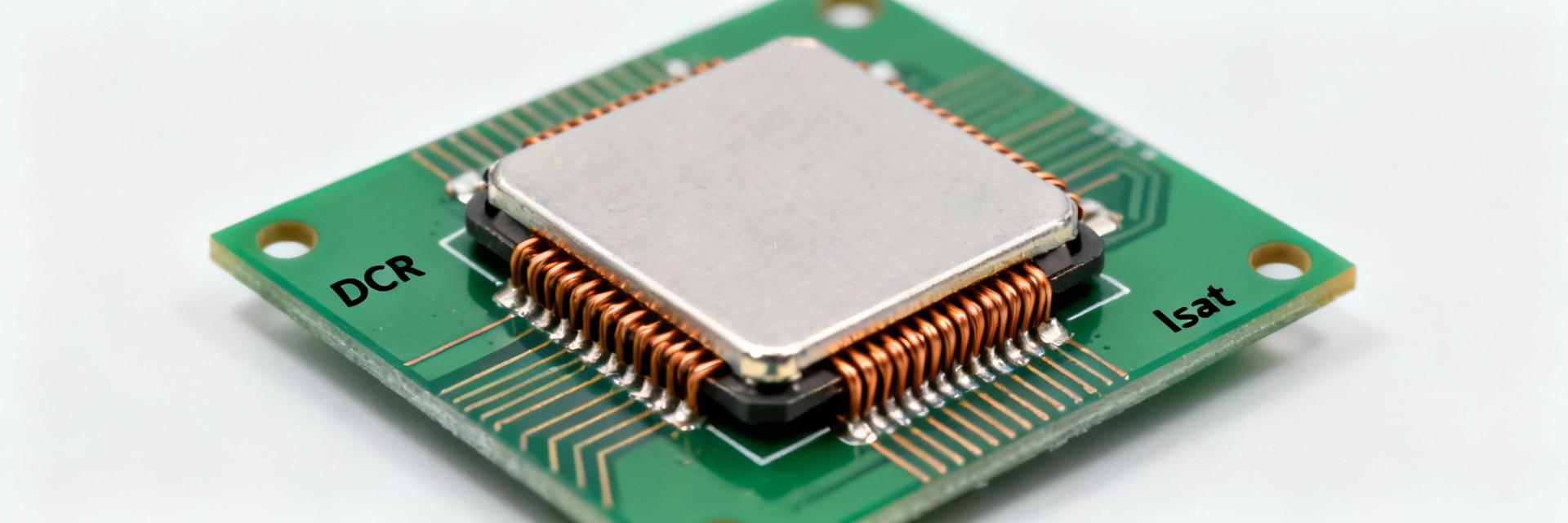
Part Identification & Typical Applications
The 7847709100 is a shielded SMD power inductor engineered for high-efficiency power-conversion circuits. It is primarily utilized in:
- •DC‑DC converters and buck regulators
- •Input/output power filters on compact SMT boards
- •High-current SMT placements near switching FETs or power ICs
At-a-glance Key Specifications
Electrical Specifications & Ratings
DC Characteristics: DCR and Current Limits
DC Resistance (DCR) is measured using a calibrated four-wire milli-ohmmeter at 20°C. The specified range of 12–18 mΩ accounts for manufacturing tolerances. The Rated Current (Irms) is dictated by the thermal threshold (ΔT ≤ 40°C), while the Saturation Current (Isat) is defined by a 10% drop in inductance under DC bias. Designers must evaluate these together to balance I²R efficiency and transient headroom.
AC Characteristics: Impedance & SRF
Impedance sweeps from 100 Hz to 30 MHz demonstrate the inductor's behavior. The Self-Resonant Frequency (SRF), typically around 10 MHz, marks the transition from inductive to capacitive behavior. Selecting an inductor with an SRF significantly higher than the converter's switching frequency is critical for maintaining circuit stability and effective EMI suppression.
Thermal & Mechanical Ratings
Thermal Dynamics
Max operating temperature is 125°C. At high ambient temperatures, Irms should be derated (typically by 20%) to ensure component longevity. Standard tests show a 40°C rise above ambient when operating at the full 6.0A rating.
Mechanical Reliability
The rectangular SMD package requires a precise land pattern. Solder reflow peaks must not exceed 260°C. Mechanical stress, such as PCB flex or extreme vibration, can lead to micro-cracking in the core or termination failures.
Test Setup & Measurement Methodology
| Parameter | Equipment / Method | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Inductance (L) | LCR Meter @ 100 kHz, 0V DC Bias | 10 μH ±20% (8.0 – 12.0 μH) |
| DC Resistance | 4-Wire Milli-ohmmeter @ 20°C | 12 mΩ (Typ) – 18 mΩ (Max) |
| Saturation (Isat) | Incremental DC Bias Injection | ≤ 10% L-drop at 8.5 A |
| Thermal Rise | Thermal Camera / Thermocouple | ΔT ≤ 40°C at 6.0 A Irms |
Application Guidance & Qualification
Design Integration Tips
Place the inductor close to the power IC and use wide, short traces to minimize parasitic resistance. Incorporate via stitching for enhanced thermal dissipation. Ensure adequate clearance from sensitive analog signals to prevent EMI interference.
Incoming Inspection Checklist
- Verify inductance and tolerance at 100 kHz.
- Perform 4-wire DCR measurement on 10-piece samples.
- Inspect visual solderability and lot traceability codes.
- Validate Isat performance on critical batch updates.
Frequently Asked Questions